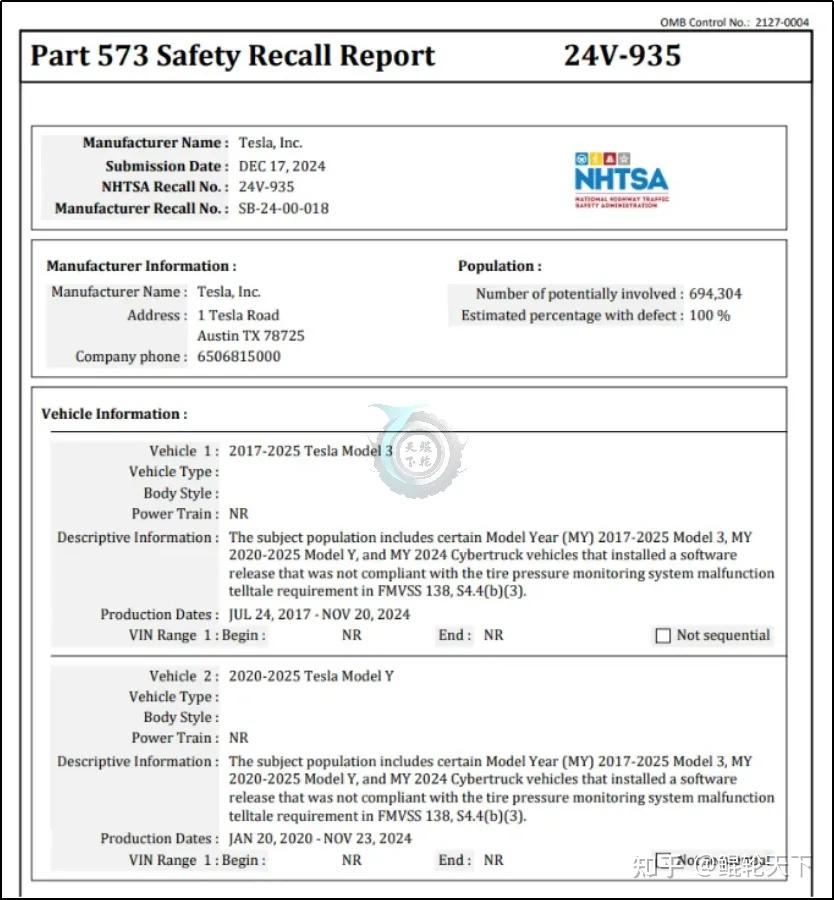
On December 21, 2024, Tesla initiated a large-scale recall due to an abnormal issue with the Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) warning light. This recall was triggered by a programming error first identified in the 2024.38.3 software update, affecting the Model 3 (2017-2025), Model Y (2020-2025), and Cybertruck (2024) models, with a total of 694,304 vehicles being recalled, approaching 700,000 pieces.
To fully understand the impact of this fault, let’s start by delving into the core working logic and key concepts of TPMS:
I. Basic Working Principle of TPMS
Currently, direct TPMS is the mainstream in automobiles, and its working process can be divided into three steps:
Sensor Collection: Each tire is equipped with a dedicated sensor that continuously measures tire pressure and temperature data. During vehicle operation or periodic wake-ups, the data is transmitted to the in-car receiver via wireless signals.
Module Processing: The receiver transmits the signals to the Body Control Module (BCM) or a dedicated TPMS control module, where the Electronic Control Unit (ECU) parses the data.
Warning Trigger: The ECU compares the measured tire pressure with the preset threshold (typically 75% of the standard pressure, i.e., 25% below the standard value). If the pressure of any tire is below the threshold, the TPMS warning light on the dashboard is immediately illuminated to alert the driver to take action promptly.
II. Key Concept: The Role of “Driving Cycle”
The working logic of TPMS is closely related to the “driving cycle,” which is typically defined as: vehicle start-up → reaching a certain driving distance (usually exceeding a certain speed, such as 25 km/h) → vehicle shutdown.
Power-saving Design: TPMS sensors are equipped with built-in lithium batteries. To extend cell lifespan, the sensors enter a sleep mode when the vehicle is stationary, and sensors send data during driving through centrifugal force or specific commands.
False Alarm Prevention Mechanism: The ECU needs to continuously receive low tire pressure signals for a certain period or confirm the fault during a complete driving cycle before officially illuminating the warning light, thus avoiding false alarms caused by temporary factors such as road bumps.
III. Core of Tesla’s Fault: Intermittent Failure of the Warning Light
The core issue of this recall is that some owners reported that the TPMS warning light might fail to illuminate between two driving cycles, preventing timely warnings of low tire pressure and posing a safety risk during driving. Based on the TPMS system structure, the causes of the fault can be summarized into four categories:
1. TPMS Sensor Fault (the most common cause)
Battery Depletion: The lifespan of the built-in lithium battery in the sensor is typically 5-10 years. As it approaches the end of its life, the battery may experience intermittent power supply issues – it may still have enough power to send signals in one driving cycle but be completely drained in the next, preventing the warning light from triggering. This is the main cause of the current fault.
Internal Component Failure: Intermittent faults in the pressure/temperature sensing chip or circuit board inside the sensor prevent accurate data collection or the transmission of low tire pressure signals.
2. Receiver/ECU Module Fault
Abnormal Signal Reception: The TPMS receiver (usually installed inside the vehicle) may fail to stably receive the weak wireless signals sent by the sensor due to aging, its own faults, or external electromagnetic interference, causing fluctuations in signal reception success rates. Software logic defect: The direct cause of this Tesla malfunction is a bug in version 2024.38.3 of the software, which may lead to abnormal ECU fault judgment logic (such as overly strict trigger conditions) or suppress alarm functions under specific operating conditions.
Hardware failure: The ECU control module itself has suffered hardware damage, preventing it from processing received signals or driving the warning light to illuminate.
3. System settings and matching issues
Sensor ID loss: After replacing the battery, TPMS module power failure or maintenance, the stored sensor ID recognition code may be lost. The ECU will treat normal sensor signals as “unknown signals” and ignore low tire pressure warnings.
Signal shielding interference: High-power electronic devices added to the vehicle (such as illegal radio transmitters, low-quality car chargers) may interfere with the TPMS operating frequency band (315MHz or 433MHz), causing alarm signals to be shielded.
4. Warning light itself failure (low probability)
If there are open circuits, loose connections, or other issues with the LED beads, driving circuits, or connection lines of the dashboard warning light, even if the ECU issues an illumination command, the warning light will not work properly. Such faults may manifest as intermittent failures
Conclusion:
This large-scale Tesla recall incident has sounded the alarm for the automotive industry regarding TPMS system safety. As a key configuration for ensuring driving safety, the stability of TPMS directly relates to the lives of drivers and passengers. Its failure may lead to excessive tire wear, blowouts, and other risks, especially at high speeds, posing a significant threat.
With the increasing electronic and intelligent levels of automobiles, TPMS products are constantly being improved and upgraded (such as adding real-time data display, abnormal tire pressure voice alerts, etc.). In the future, TPMS technology will be further integrated with autonomous driving, vehicle networking, and other functions as an important part of the intelligent travel safety system, which change our solution scheme and cognitive awareness.
Post time: Nov-21-2025